Why is preconception care important and who should participate in this type of service?
- helps make decisions about reproductive future
- how to prevent unintended pregnancy, risk management
- identify healthy behaviors
- must be before 17-56 days
- all women from menarche to menopause
- especially if problems with previous pregnancy
- helps to minimize malformtions
What keeps women from seeking health care?
Many factors, but three important ones are:
- finances
- culture
- gender
What are the components of the menstrual cycle, the ovarian cycle and the hypothalamic-pituitary cycle.
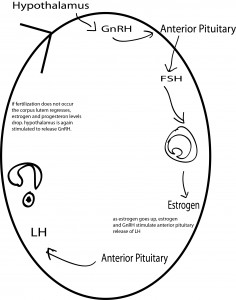
Menstrual cycle – complex interplay of events that occur simultaneously in the endometrium, hypothalamus and pituitary glands, and ovaries.
Menstruation – uterine bleeding beginning 14 days after ovulation. Average length is 28 days. Average length of menstrual flow is 5 days. Average blood loss is 50 ml.
Hypothalamic-pituitary cycle – near the end of the menstrual cycle serum estrogen and progesterone fall stimulating secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This stimulates pituitary secretion of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). FSH stimulates the production of estrogen. This triggers the release of LH (luteinizing hormone) which stimulates the expulsion of the ovum. LH peaks at day 13-14 (when ovum is released). If fertilization does not occur the corpus luteum regresses, progesterone and estrogen decline, menstruation occurs. The hypothalamus will be triggered to release GnRH once again.
Ovarian Cycle – Follicles mature within each ovary under the influence of FSH and estrogen. The increase in LH causes ovulation to occur and the empty follicle changes into the corpus luteum. After ovulation, estrogen levels decrease. The luteal phase begins immediately after ovulation and terminates at the start of menstruation. The corpus luteum secrets estrogen and progesterone. If the ovum does not implant in the endometrium, steroid levels will fall and menstruation will occur.
Endometrial Cycle – Consists of four phases; the menstrual phase, the proliferative phase, the secretory phase, the ischemic phase.
- Menstrual Phase – shedding of two thirds of the endometrium.
- Proliferative Phase – rapid growth lasting from the 5th day until ovulation.
- Secretory Phase – from ovulation until 3 days before the next menstrual phase.
- Ischemic Phase – blood supply to endometrium is blocked resulting in necrosis, menstrual bleeding begins, marking day 1.
How often do women need a pap and pelvic exam, mammography, colon cancer screening and immunizations.
- Pap Smear – should be screened at least every 3 years from 18-65 (MMCI protocol). American Cancer Society – sexually active for three years or over 21 to have yearly pap smear. After 30, after 3 normal tests, every 2-3 years.
- Pelvic Exam – every 3 years from age 20-40 and every 1-3 years after that.
- Mammography – every 1-2 years from age 35 and on.
- Colon Screening – yearly from age 45 and on.
- Immunizations – at risk until 65 then Oct. & Mar. each year.
What is amenorrhea and dysmenorrheal? What are the common causes?
- Amenorrhea – the absence of menstrual flow.
- Criteria:
- absence of menarche by age 14
- absence of menses by age 16
- 6 month cessation of menses
- Common Causes:
- interruption in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian-uterine cycle.
- hypo or hyperthyroidism
- type 1 diabetes
- meds like phenytoin
- eating disorders
- exercise
- stress
- oral contracptives
- Nursing Management:
- counseling and education
- Dysmenorrhea – pain during or before menstruation.
- Primary Dysmenorrhea – associated with ovulatory cycles
- Management:
- depends on severity response
- education and support
- heat, massage, rubbing the abdomen, biofeedback
- Secondary Dysmenorrhea – acquired pain that develops later in life (after 25)
- Causes:
- adenomyosis
- endometriosis
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- endometrial polyps
- Management:
- Removal of the underlying pathology
What are PMS and PMDD, their causes and some common treatments.
- PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome) – mood and somatic symptoms that occur with menstrual cycles.
- Symptoms:
- fluid retention
- behavioral or emotional changes
- premenstrual cravings
- headache
- fatigue
- backache
- Causes: (unknown)
- Psychological component
- Cultural beliefs
- Most likely not a single disorder, but a collection of different problems.
- Treatment:
- any change that improves a womans control over her life.
- Education is key
- diet and exercise
- do not smoke
- limit sugar, salt, and alcohol, and caffeine
- eat more veggies, whole grains
- three small meals and three snacks a day
- nutritional supplements that help with PMS
- calcium
- magnesium
- vitamin B6
- evening primrose oil
- medication
- diuretics
- NSAIDs
- progesterone
- OCPs
- Fluoxetine (SSRI)
- PMDD – a severe variant of PMS
- women more markedly irritable
- dysphoria
- mood lability
- anxiety
- fatigue
- appetite changes
- sense of feeling overwhelmed
What is endometriosis? What problems can it cause? What are some treatments?
Endometriosis – presence and growth of endometrial tissue outside of the uterus. It affects about 5-15% of women in reproductive age. Etiology ad pathology are unknown. Symptoms include pelvic pain and can vary in intensity, painful intercourse, dysmenorrhea, pain that radiates to the thighs. Endometriosis can lead to impaired fertility due to adhesions around the uterus that change the position of the uterus.
Treatments for endometriosis include (based on severity); NSAIDs, OCPs with low estrogen to progesteron ratio to shrink endometrial tissue. Hormone therapy is used for women that wish to become pregnant . Surgical intervention is often used for severe, acute, or incapacitating symptoms. The only definite cure is hysterectomy. Laser surgery can be attempted to remove as much endometrial tissue as possible while still preserving function.
How is HIV transmitted and how does it affect pregnancy?
Transmission of HIV occurs through body fluids. The women should be tested for other possible STIs. They need nutritional support and education about diet, proper rest, and stress reduction. Weight gain during pregnancy can be a challenge for the HIV-infected patient.
Contraception, Abortion, and Infertility
What is contraception?
Contraception is the intentional prevention of pregnancy during sexual intercourse.
Explain the following are used to prevent pregnancy, what their common side effects are, and issues that affect their effectiveness.
a. Coitus interruptus
Involves “pulling out” the penis from the vagina prior to ejaculation and moving it away from her external genitalia. Effectiveness depends on the males ability to control orgasim. It is free and requires to drugs. 27% of women will experience an unintended pregnancy within the first year of this method.
b. Fertility Awareness Methods (in general)
Identify the beginning and end of the fertile period of the menstrual cycle. Three phases:
- Infertile phase: before ovulation.
- Fertile phase: about 5-7 days around the middle of the cycle.
- Infertile phase: after ovulation.
Disadvantage: must keep a strict schedule, decreased effectiveness in women with irregular cycles, decrease ability for spontaneous sex, do not protect against STIs
Failure rate of 25%
c. Condoms
Failure rate is 15%(male condom), 21% (female condom).
Advantage: protect against STIs
Disadvantage: latex allergy, cost, must be used consistently
d. Diaphragms, cervical caps, and sponges
Failure rate: 16%
Advantage: washable and reusable
Disadvantage: cost, works better when used with spermicide gel, exam to insure fit, must insert and remove, decreased spontaneity
e. Oral contraceptives
Failure rate: 8%
Suppress the action of the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, alter maturation of endometrium.
Advantages: does not relate to the sexual act, decreased menstrual flow, protect against endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer.
Disadvantages: medical screening needed, side effects, cost, breast tenderness, irregular bleeding
f. Bilateral Tubal Ligation
Failure rate: 1%
Uterine tubes are severed and ligated can be completed on an out patient basis. Complications include all other surgery complications, anesthesia, infection, hemorrhage, and trauma to other organs.
g. Vasectomy
Failure rate: 0.15%
Sealing, tying, or cutting of the vas deferens that inhibits the travel of sperm from testes to penis. Normal surgery complications can occur. Scrotal support may be needed.
What are the nursing considerations for the woman who elects to have an abortion?
The nurses primary role in abortion in to educate and provide support measures as needed.
How is infertility diagnosed?
Evaluation of the cervix, uterus, tubes, and peritoneum, detection of ovulation, assessment of immunological compatibility, and assessment of psychogenic factors.
What are common male and female causes of infertility?
Female Causes:
- Ovarian Factors
- developmental anomalies
- anovulation (primary)
- pituitary or hyopthalamus disorders
- adrenal gland disorder
- congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- anovulation (secondary)
- disruption of hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
- amenorrhea
- Premature ovarian failure
- increased prolactin levels
- Uterine, Tubal, and Peritoneal Factors
- developmental anomalies
- tubal motility reduced
- inflammation
- endometriosis
- chronic cervicitis
- hostile or inadequate cervical mucus
- Other Factors
- nutritional deficiencies
- thyroid dysfunction
- idiopathic condition
Male Causes:
- Structural or Hormonal Disorders
- undescended testes
- hypospadias
- varicocele
- lessions of the vas deferens
- Other Factors
- STIs
- Exposure to workplace hazards
- Nutritional deficiencies
- antisperm antibodies
What are emotional and medical risks for fertility treatments?
Genetics, Conception, and Fetal Development
What are the structures of the fetal circulatory/respiratory system that support the fetus in utero? What is there function?
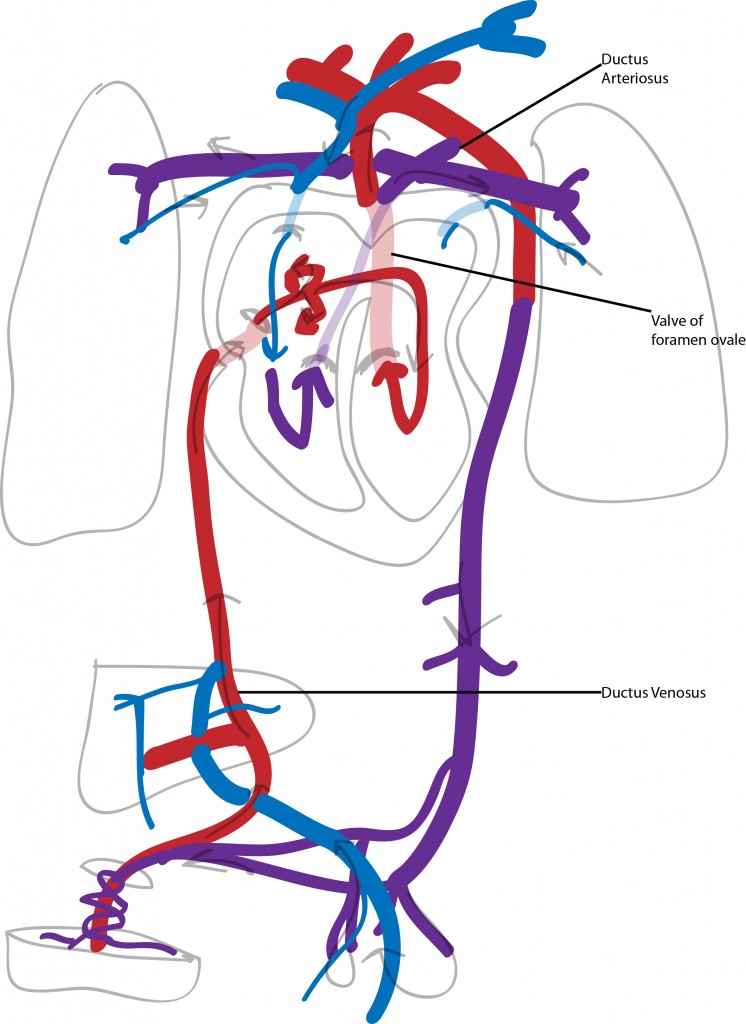
The above diagram depicts fetal circulation.
Key Points:
- Two arteries which carry blood to back to the placenta
- 1 vein which delivers blood to the fetus
- It is the first organ system to develop in the human
- Blood vessel and blood cell formation begins in the third week
- Heart begins to beat in the 3rd week
- Heart is developmentally complete by the end of the embryonic stage
- Lungs do not function for respiratory exchange
- Ductus arteriosus bypasses the lungs
- Blood travels through umbilicus through the liver through the ductus venosus into the inferior vena cava
- Mixes with deoxygenated blood in the liver
- Travels through right atrium through the foramen ovale
- Enters the aorta and supplies the head, heart, neck, arms
- Returns to the heart through the superior vena cava
- Small amount passes through the lungs
- Majority travels through the aorta through the ductus arteriosus
- This oxygen poor blood travels to the legs, gut, kidneys and on through the umbilicus into the placenta
Where does fertilization happen?
Fertilization occurs in the outer 3rd (ampulla) of ther uterine tube.
When the sperm penetrates the membrane surrounding the ovum they are both enclosed in the membrane and it become impenetrable to other sperm. The tail of the sperm degenerates. The nuclei fuse and combine chromosomes, the zygote is formed.

Where and when does implantation happen?
Implantation occurs about 6-10 after conception. Chorionic villi develop out of the trophoblast which allow for it to attach to the blood filled spaces of the endometrium.
This usually occurs in the anterior or posterior fundal region.
When is the most dangerous time for the fetus in relation to development?
The embryonic stage (day 15 -8 weeks). Up until about 12 weeks is the highly sensitive period for organ development.
What is the function of the amniotic fluid?
The amniotic fluid is derived through diffusion of the mothers blood and from urine of the fetus.
Normal amniotic fluid levels are: 800-1200ml
<300 ml (olighydramnios) renal abnormalities
>2 L (hydramnios) GI abnormalities
Functions of the amniotic fluid:
- maintain body temp
- oral fluid and repository for waste
- cushion
- freedom of movement
- keeps fetus from tangling
What is the function of the placenta?
Maternal-placental-embryonic circulation is in place by day 17, when the heart begins to beat.
Function:
- Maternal blood supplies oxygen and nutrients
- Waste products and CO2 diffuse into the maternal blood
- Endocrine gland: produces hormones that maintain pregnancy
- Storage of nutrients for fetal needs (carbs, proteins, calcium, iron)
How many veins and arteries does the umbilical cord contain? Which is carrying oxygenated blood from the mom to the fetus?
2 arteries – carry blood back to the placenta
1 vein – supplies blood to the embryo
What is the difference between dizygotic twins and monozygotic twins?
Dizogotic: 2 ova, 2 amnions, 2 placenta, fraternal, do not look alike
Monozygotic: 1 ova which divides, same sex, same genotype
When does the fetal heart begin to beat?
The fetal heart will begin to beat by the 3rd week. It will develop into 4 chambers by the 4th – 5th week.
When is it possible to tell sex of the fetus?
9-12 weeks
When are respiratory movements seen for the first time?
Respiratory development occurs between 4 – 17 weeks. Movements can be seen via ultrasound as early as 11 weeks.
When is the L/S ratio 2:1?
These are two important alveolar surfactants. Once the ratio between the two is 2:1 it is an indication that the fetal lungs have matured to a sufficient point. This occurs around week 35.
When can the baby hear?
The baby will begin to respond to external sounds as early as 24 weeks.
Resources: Maternity Nursing 7th edition. Lowdermilk & Perry. Mosby Elsevier Publishing.